In injection molding, cooling plays a critical role in determining the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of the production process. The cooling phase accounts for a significant portion of the total cycle time, making it essential to optimize cooling strategies to achieve faster production rates and high-quality molded parts. One of the most effective ways to enhance cooling efficiency is through well-designed cooling channel injection molding techniques. Cooling channels are integrated into the mold structure to regulate the temperature of the molten plastic, ensuring uniform cooling and preventing defects such as warping, shrinkage, and residual stress. Proper cooling channel in mold design leads to improved part quality, reduced cycle times, and lower manufacturing costs. This article explores the principles, types, design considerations, and benefits of optimized cooling channels in injection molding.
Importance of Cooling Channels in Injection Molding
The cooling process begins as soon as molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity. If cooling is not controlled effectively, several defects can occur, including inconsistent part dimensions, sink marks, and internal stress that compromises part durability. An efficient mold cooling channel system ensures that the entire part cools at a uniform rate, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring dimensional stability. In high-volume production environments, cooling time is a major factor influencing overall productivity. A poorly designed cooling system can lead to extended cycle times, increasing production costs and reducing throughput. By optimizing the mold cooling channel design, manufacturers can significantly shorten cycle times while maintaining product quality, leading to improved operational efficiency.
Types of Cooling Channels in Mold Design
Conventional Cooling Channels
Conventional cooling channels are straight or circular passages drilled into the mold to allow coolant, typically water or oil, to flow through and extract heat from the molten plastic. These channels are relatively easy to manufacture and are effective for simple mold designs. However, they may not provide uniform cooling in complex parts with intricate geometries.
Conformal Cooling Channels
Conformal cooling channels are designed to follow the contours of the mold cavity, ensuring more uniform heat dissipation. These channels are typically created using advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing or additive manufacturing. Conformal cooling allows for more efficient heat transfer, reducing cycle times and minimizing defects caused by uneven cooling.
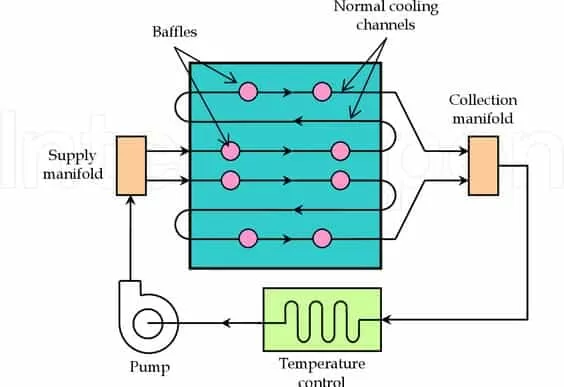
Baffle and Bubbler Cooling Systems
Baffles and bubblers are used in molds where direct cooling channels are difficult to implement. Baffles split the coolant flow into two directions within a single cooling channel, enhancing heat exchange. Bubblers introduce a tube with small openings that allow coolant to circulate within tight mold areas, improving localized cooling efficiency.
Heat Pipes and Thermal Pins
Heat pipes and thermal pins are used in molds that require rapid heat dissipation in specific regions. These components contain a fluid that absorbs heat from the mold and transfers it to an external cooling system. Heat pipes are particularly useful for high-precision applications where temperature control is critical.
Key Considerations in Mold Cooling Channel Design
Optimal Channel Placement
The placement of cooling channels must ensure uniform heat removal across the entire mold cavity. Channels that are too far from the molded part may lead to inefficient cooling, while those too close may cause localized temperature drops, leading to stress and warping. The ideal channel placement depends on the part geometry, material properties, and cycle time requirements.
Channel Diameter and Flow Rate
The diameter of cooling channels affects the flow rate of the coolant and the overall efficiency of heat dissipation. Larger channels allow for higher coolant flow but may take up more mold space. Smaller channels can provide precise cooling but may create resistance to coolant flow. Balancing channel size and flow rate is essential for achieving optimal cooling performance.
Material Selection for Molds
Mold materials play a crucial role in heat transfer efficiency. High thermal conductivity materials, such as beryllium copper and aluminum, enhance heat dissipation and improve cooling performance. Steel molds, commonly used for their durability, may require advanced cooling channel designs to achieve efficient heat transfer.
Cooling Circuit Design
A well-structured cooling circuit ensures that coolant flows evenly throughout the mold. Series and parallel cooling circuits are commonly used configurations. Series circuits direct coolant through multiple channels sequentially, while parallel circuits split coolant flow across different channels simultaneously. Parallel circuits are generally preferred for maintaining uniform cooling.
Benefits of Optimized Cooling Channel Injection Molding
Reduced Cycle Time
Efficient cooling channels accelerate the solidification of the plastic part, allowing for quicker ejection and shorter cycle times. This leads to increased production efficiency and lower per-part manufacturing costs.
Improved Part Quality
Uniform cooling minimizes defects such as warpage, shrinkage, and internal stresses, resulting in higher-quality molded parts with better dimensional accuracy. Consistent cooling also enhances the mechanical properties of the final product.
Energy and Cost Savings
Shorter cycle times lead to reduced energy consumption per part, lowering operational costs. Additionally, fewer defective parts reduce material waste and rework expenses, improving overall profitability.
Enhanced Mold Longevity
Proper cooling channel design reduces thermal stress on the mold, preventing premature wear and extending mold lifespan. This reduces maintenance costs and ensures long-term production efficiency.
The design and implementation of cooling channel injection molding systems play a crucial role in achieving high-quality, cost-effective, and efficient production processes. By optimizing cooling channel in mold configurations, manufacturers can significantly enhance cooling performance, reduce cycle times, and improve part quality. Advanced mold cooling channel designs, such as conformal cooling and baffle systems, offer superior heat dissipation compared to traditional methods. Additionally, selecting the right mold cooling channel design based on part geometry, material properties, and production requirements ensures consistent cooling and defect-free molding. As injection molding technology continues to evolve, integrating innovative cooling solutions will remain a key factor in optimizing manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Innovative Cooling Techniques for Enhanced Efficiency
As injection molding technology advances, manufacturers are continuously exploring new ways to improve cooling efficiency. Traditional cooling methods, while effective, may not always provide the most optimized heat dissipation. Advanced cooling techniques such as conformal cooling, vacuum cooling, and pulsed cooling have emerged as innovative solutions to improve cycle times and product quality.
Conformal cooling, as mentioned earlier, involves designing cooling channels that follow the contours of the molded part. Unlike conventional straight-drilled channels, conformal cooling ensures that heat is removed evenly across complex geometries. This technique is particularly beneficial for intricate plastic parts where uniform cooling is critical to maintaining dimensional accuracy. The use of 3D-printed mold inserts has enabled greater flexibility in conformal cooling designs, leading to improved thermal efficiency.
Vacuum cooling is another technique that accelerates heat removal from the mold by reducing the pressure inside the cooling channels. This method enhances the cooling rate by allowing water or other coolants to absorb heat more efficiently. Similarly, pulsed cooling cycles the coolant flow in short bursts rather than maintaining a continuous flow. This process optimizes heat exchange and prevents coolant overheating, leading to better overall cooling performance.
Cooling Channel Placement and Optimization Strategies
Uniform Heat Removal Across the Mold
For efficient cooling, channels must be placed strategically to remove heat uniformly across the entire mold surface. Uneven cooling can result in stress buildup, leading to defects such as warping, sink marks, and voids. Engineers use thermal imaging and simulation software to analyze heat distribution and adjust cooling channel placement accordingly.
One effective strategy is to position cooling channels as close as possible to the mold cavity without compromising structural integrity. This allows for faster heat extraction while maintaining mold durability. Additionally, varying channel depths in different mold sections can help compensate for areas that retain more heat.
Balancing Flow Rate and Coolant Temperature
The effectiveness of cooling channels also depends on the balance between flow rate and coolant temperature. If the coolant moves too slowly, it absorbs excessive heat and becomes less effective as it travels through the mold. On the other hand, a flow rate that is too high may not allow sufficient heat transfer to occur. The ideal cooling system maintains a consistent temperature difference between the inlet and outlet, ensuring efficient heat exchange throughout the mold.
Multi-Zone Cooling Systems
In complex injection molds, a single cooling circuit may not be sufficient to provide uniform temperature control. Multi-zone cooling systems divide the mold into separate cooling regions, each with independently controlled temperature settings. This approach is particularly useful for large molds or those with varying wall thicknesses, as it allows for customized cooling tailored to different sections of the part.
Multi-zone cooling reduces internal stresses by ensuring that thicker sections cool at the same rate as thinner sections. This technique is widely used in automotive and medical molding applications, where high precision and consistency are required.
Materials Used in Mold Cooling Channel Design
The material used in molds significantly impacts cooling efficiency. High thermal conductivity materials, such as beryllium copper and aluminum alloys, are often used in mold inserts to improve heat transfer. These materials allow for faster cooling, reducing cycle times and improving part quality.
Steel remains the most common mold material due to its durability, but it has lower thermal conductivity than aluminum or copper-based alloys. To compensate, manufacturers use advanced cooling channel designs or incorporate high-conductivity inserts in critical areas. Additionally, coatings such as nickel or ceramic layers can enhance wear resistance while maintaining thermal efficiency.
The Role of Die Casting Manufacturers in China in Mold Cooling Innovation
While plastic injection molding dominates many industries, metal components often require die casting processes. Die casting manufacturers in China have played a key role in advancing mold cooling technologies for both plastic and metal molding applications. Die casting requires rapid cooling to maintain dimensional accuracy and reduce cycle times, similar to plastic injection molding. Many of the cooling techniques used in injection molding, such as conformal cooling and vacuum-assisted cooling, have been adapted from advancements in die casting. The expertise of die casting manufacturers in China has contributed to the development of hybrid molding solutions that integrate both plastic and metal components. By leveraging advanced cooling channel designs, these manufacturers have improved production efficiency and product quality across multiple industries.
Common Defects Caused by Poor Cooling Channel Design
Even minor inconsistencies in cooling channel design can lead to defects in injection-molded parts. Some of the most common defects include:
- Warping – Occurs when different sections of the part cool at different rates, leading to internal stress and deformation.
- Sink Marks – Form when the outer surface of the part cools faster than the inner material, causing a visible depression.
- Voids and Air Pockets – Develop when trapped air is unable to escape due to poor cooling channel placement.
- Residual Stress Cracking – Results from uneven cooling, which creates internal stress that weakens the part over time.
Optimizing cooling channel placement and using advanced cooling techniques can significantly reduce these defects, ensuring consistent part quality.
Future Trends in Mold Cooling Channel Design
The future of mold cooling channel design is moving toward greater automation and precision. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being integrated into cooling optimization processes. AI-powered systems analyze real-time temperature data and adjust cooling parameters dynamically to maintain optimal conditions. Another exciting development is the use of smart molds equipped with embedded temperature sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity. These sensors provide continuous monitoring of cooling performance, allowing manufacturers to detect potential issues before they affect production quality. Sustainable cooling solutions are also gaining attention, with many manufacturers exploring eco-friendly coolant options and energy-efficient cooling systems. Water-saving techniques and closed-loop cooling circuits help reduce environmental impact while maintaining high-performance cooling efficiency.
Conclusion
The role of cooling channel injection molding in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated. By optimizing cooling channel in mold designs, manufacturers can significantly enhance productivity, reduce cycle times, and improve product quality. Advanced cooling strategies such as conformal cooling, multi-zone temperature control, and vacuum-assisted cooling continue to push the boundaries of efficiency in injection molding. Additionally, insights from die casting manufacturers in China have contributed to mold cooling innovations that benefit both plastic and metal manufacturing industries. As technology evolves, the integration of AI-driven cooling management and sustainable cooling solutions will further improve efficiency, making injection molding more precise, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. By staying ahead of advancements in mold cooling channel technology, manufacturers can maintain a competitive edge in the industry, ensuring that every part produced meets the highest standards of quality and performance.